Your brain is constantly active, even when you’re asleep — and this activity generates electrical patterns known as brain waves. These waves are not just abstract signals; they directly influence how you think, feel, focus, sleep, and even how you connect with others.
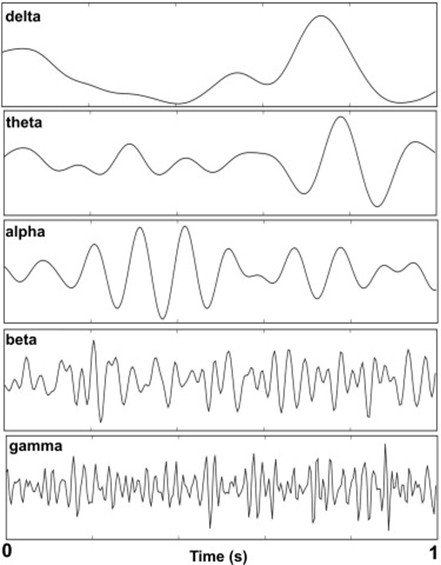
There isn’t just one type of brain wave — in fact, your brain produces five main types, each with its own frequency and function:
Delta for deep sleep and physical healing
Theta for dreams, intuition, and emotional processing
Alpha for calm awareness and mental clarity
Beta for alert thinking, learning, and solving problems
Gamma for memory, insight, and high-level mental performance
A healthy brain doesn’t rely on just one type — it maintains a dynamic balance among all of them, shifting as needed based on what you’re doing. Like a skilled orchestra, the brain’s wave activity must be coordinated and adaptable. When the balance is disrupted — for example, too much beta leading to anxiety, or too much theta causing brain fog — mental and emotional health can suffer.
Understanding brain waves is essential if you want to optimize your focus, reduce stress, sleep better, and feel more in control of your emotions. Whether you’re meditating, studying, or just trying to quiet your mind, learning how brain waves work gives you a powerful window into your own mental landscape — and tools to shift it.
| Wave | Frequency (Hz) | Role | When it’s healthy to have more of it |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta | 0.5–4 Hz | Deep sleep, healing | During deep, restorative sleep. Slowest brain wave, found in infants and young children. Deepest level of relaxation and recovery. Also seen in brain injuries, learning problems, inability to think, and severe ADHD. |
| Theta | 4–8 Hz | Creativity, intuition, emotional processing | During meditation, daydreaming, or just before sleep. Supports memory processing, emotional release, and intuitive insight. Too much → brain fog, difficulty focusing. |
| Alpha | 8–12 Hz | Calm focus, relaxed alertness | When you’re relaxed but aware — like walking or reading calmly. Associated with a clear and peaceful state of mind. Healthy alpha = calm focus + emotional regulation |
| Beta | 12–30 Hz | Active thinking, focus, logic | While solving problems, working, or engaging in mental activity. Too much → anxiety, overthinking. The right amount helps maintain focus and productivity. |
| Gamma | 30–100 Hz | High-level cognition, memory, and insight | During peak focus, learning, or spiritual awareness. Fastest brainwave frequency. Associated with advanced mental processing and heightened awareness. Healthy brains show gamma bursts during insight or integration of new information. |
🧠 Example of Healthy Brainwave Balance (awake adult at rest):
- ~50% Alpha
- ~30% Beta
- Small % Theta
- Very little Delta
- Gamma bursts during focused tasks
What happens when there’s an imbalance?
| Too Much of… | Possible Issue |
| Beta | Anxiety, tension, overthinking (Racing thoughts) |
| Theta | Brain fog, attention problems, Spaciness, dissociation |
| Delta (when awake) | Depression, fatigue, Brain fog, sluggish thinking |
| Alpha (too much when trying to focus) | Spaciness, lack of motivation (Due to dopamine drop) |
| Gamma (if too low) | Memory or cognitive problems, lack of insight |
Too little delta: Poor sleep, low healing, fatigue
Ways to Balance Delta:
- 🌙 Get deep, uninterrupted sleep — use blackout curtains, magnesium, and a fixed sleep schedule
- 💤 Weighted blankets — help ground the nervous system and increase delta in sleep
- 📵 Avoid screens 1 hour before bed — blue light suppresses delta-producing sleep
- 🎧 Binaural beats (0.5–4 Hz) — train your brain into delta using headphones at night
- 🧘♀️ Yoga Nidra or body scan meditations — promotes natural delta rhythms
————————
Too little theta: Creative block, lack of emotional access
Ways to Balance Theta:
- 🎨 Creative play — paint, write, sing, or daydream (mind-wandering activates theta)
- 🧘♂️ Guided meditation or visualization — especially right before sleep
- 📓 Journaling from the subconscious — write without thinking too much (stream of consciousness)
- 🧠 Limit alcohol/cannabis — both can increase theta too much, leading to fogginess
- 🏃♀️ Light cardio before studying — boosts alertness and reduces excess theta
———————————-
Too little alpha: Tension, stress, difficulty relaxing
Ways to Balance Alpha:
- 🌿 Nature walks — calm movement in natural settings increases alpha naturally
- 📵 Tech breaks — reduce mental overstimulation by unplugging daily
- 🎧 Alpha brainwave music (8–12 Hz) — use during reading, reflection, or journaling
- 🧘♀️ Mindful breathing — 5 minutes of slow nasal breathing calms the brain
- 🛀 Hot baths or saunas — physical relaxation boosts alpha activity
————-
Too little beta: Trouble focusing, mental sluggishness
Ways to Balance Beta:
- ✍️ Brain dumping — write down everything you’re thinking before starting a task (calms excess beta)
- 🧊 Cold face rinse or shower — slows down overactive beta and grounds you
- ⏳ Pomodoro technique — 25 min focus, 5 min rest (prevents beta burnout)
- 🍵 Avoid too much caffeine — overstimulates beta waves
- 🧠 Neurofeedback (Beta training) — helps increase beta if you’re too sluggish
🔹 Too much gamma Rare): Hyperstimulation, insomnia
Ways to Balance Gamma:
- 🧠 Learning something new — puzzles, languages, strategy games stimulate gamma
- 🧘♀️ Loving-kindness meditation — shown to increase gamma (especially in monks!)
- 🎵 High-frequency sound therapy — some sound tools target gamma enhancement
- 🌞 Get morning sunlight — supports brain activation and neurochemical balance
- 🧬 Supplement: L-theanine + caffeine — gentle alertness that may support gamma function

Helping clients improve brain health and prevent Alzheimer’s through expert coaching.
Navigate

Helping clients improve brain health and prevent Alzheimer’s through expert coaching.
Navigate

Helping clients improve brain health and prevent Alzheimer’s through expert coaching.
